CYBERMED LIFE - ORGANIC & NATURAL LIVING
CYBERMED LIFE - ORGANIC & NATURAL LIVING
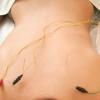 Electroacupuncture is a form of acupuncture where a small electric current is passed between pairs of acupuncture needles. According to some acupuncturists, this practice augments the use of regular acupuncture, can restore health and well-being, and is particularly good for treating pain. There is evidence for some efficacy (when used in addition to antiemetics) in treating moderate post-chemotherapy vomiting, but not for acute vomiting or delayed nausea severity.
Electroacupuncture is a form of acupuncture where a small electric current is passed between pairs of acupuncture needles. According to some acupuncturists, this practice augments the use of regular acupuncture, can restore health and well-being, and is particularly good for treating pain. There is evidence for some efficacy (when used in addition to antiemetics) in treating moderate post-chemotherapy vomiting, but not for acute vomiting or delayed nausea severity.
"Electroacupuncture is quite similar to traditional acupuncture in that the same points are stimulated during treatment. As with traditional acupuncture, needles are inserted on specific points along the body. The needles are then attached to a device that generates continuous electric pulses using small clips. These devices are used to adjust the frequency and intensity of the impulse being delivered, depending on the condition being treated. Electroacupuncture uses two needles at time so that the impulses can pass from one needle to the other. Several pairs of needles can be stimulated simultaneously, usually for no more than 30 minutes at a time."
That article adds:
"According to the principles of traditional Chinese medicine, illness is caused when chi does not flow properly throughout the body. Acupuncturists determine whether chi is weak, stagnant or otherwise out of balance, which indicates the points to be stimulated. Electroacupuncture is considered to be especially useful for conditions in which there is an accumulation of chi, such as in chronic pain syndromes, or in cases where the chi is difficult to stimulate."
Electroacupuncture is also variously termed EA, electro-acupuncture or incorporated under the generic term electrotherapy.
Electroacupuncture according to Voll (EAV) claims to measure "energy" in acupuncture points and to diagnose ailments. Some devices are registered in FDA as galvanic skin response measuring devices; they may not be used in diagnosis and treatment. Units reportedly sell for around $15,000 and are promoted for diagnosis of conditions including "parasites, food and environmental sensitivities, candida, nutritional deficiencies and much more." It is promoted for diagnosis of allergies.